Related articles: Latitude studies, Palliative vs. curative treatments
Table of Contents
Sunshine/light exposure as therapy
According to the Marshall Pathogenesis, light-related changes in mood can be attributed to fluctuations in 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25-D). Such reactions exist in people who suffer from “seasonal affective disorder” as well as those who are addicted to or dependent upon tanning.
Contrary to popular belief, epidemiological research points to an increase in suicide across countries during the beginning of the summer months when people tend to get more light exposure.
Light exposure does nothing to resolve underlying disease state and can actually delay progress for Marshall Protocol (MP) patients. Certainly prolonged light exposure has been shown to increase skin melanoma – the World Health Organization now categorizes tanning beds under the highest cancer risk category.1)
MP patients who have completed the treatment have been able to attest to the fact that sunshine is not necessary for good health or happiness.
Despite what some researchers have argued, latitude studies that try to tie ambient solar UV radiation to prevalence of disease have been inconclusive.
Sunshine and suicide
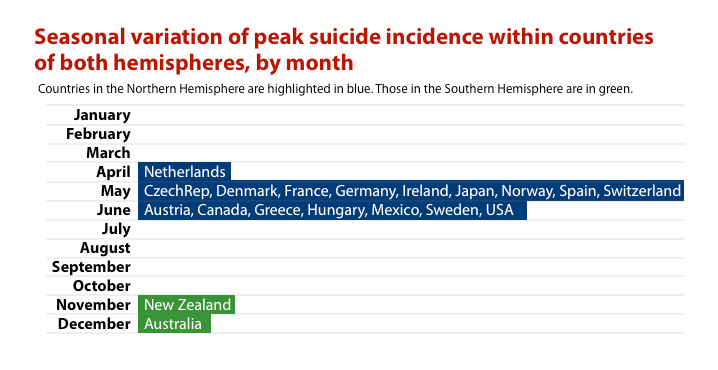
In spite of a widespread belief that the peak occurs in late autumn and early winter,2) a positive correlation between sunlight and suicide has been demonstrated by several researchers.
We found a remarkably consistent pattern of seasonality with peak incidence around June in the northern hemisphere and December in the southern hemisphere. Moreover, there was a positive association between the seasonal amplitude of suicide (measured by relative risk) and total sunshine in the corresponding country. These findings indicate that sunshine may have a triggering effect on suicide….
Eleni Petridou, et al 3)
Petridou's work is striking, because it identifies an effect for all 20 countries studied:
Increased summer incidence of suicide has also been identified in other countries including Finland,4) Norway,5) Belgium,6) France,7) Italy,8) Japan,9) USA,10) Lithuania,11) Switzerland,12) Chile,13) and South Africa.14)
In many, if not all, of these studies the increased incidence of suicide was shown to be independent of an increase in homicide.
Sunlight can be immunosuppressive
Related section: Effect of light on the skin
Phototherapy suppresses immunity which can lead to the progression of other infections such as human papilloma virus (HPV). A 2010 study used a nested polymerase chain reaction, to analyze skin biopsies taken a from 20 psoriasis patients under phototherapy (UVB) and 20 untreated psoriatic patients. The authors were able to detect viruses in 60% of the treatment but in none of the controls.15)
1,25(OH)2D3 resulted in suppression of proinflammatory cytokineAny of various protein molecules secreted by cells of the immune system that serve to regulate the immune system. response in vitro First, we carried out LPS and Pam3Cys stimulation on PBMC with the addition of 100 nM 1,25(OH)2D3. After 24 h, IL-6 secretion was reduced by 53% and 29% upon Pam3Cys and LPS stimulation, respectively, in the cells treated with 1,25(OH)2D3 (Fig. 1a). A significant drop in TNF-α production by 17% (Pam3Cys stimulation) and 35% (LPS stimulation) was also observed with 1,25(OH)2D3 at 24 h. Having demonstrated that 1,25(OH)2D3 had the capacity to modulated IL-6 and TNF-α response in vitro, and with the understanding that physiological vitamin D3 levels in the body may vary through the seasons, we validate these observations in vivoA type of scientific study that analyzes an organism in its natural living environment. in a cohort of healthy volunteers.16)
A 2011 study by Damian et al. concluded that exposure to sunlight even at suberythemal levels – sunlight which doesn't cause redness – is “profoundly immunosuppressive” in humans and that it is the immune-suppressive effects of sunlight that play a central role in skin carcinogenesis.17)
Certain support for this study comes from a 2011 Australian paper that found that 8 week old mice given a single exposure of ultraviolet radiation had suppressed immunity.18)
By providing temporary symptom relief, tanning may be addictive
The Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) is at the heart of innate immunity, transcribing over 913 genes. In a healthy person, conversion of additional 25-D into 1,25-D leads to the transcription of antimicrobial peptides and bacterial die-off. In a patient sick with chronic disease the VDR is blocked by bacterial ligands and levels of 1,25-D escalate to the point where other receptors are blocked from transcribing their antimicrobial peptides. An inactive immune response leads to a reduction in immunopathologyA temporary increase in disease symptoms experienced by Marshall Protocol patients that results from the release of cytokines and endotoxins as disease-causing bacteria are killed. and consequently feelings of temporary well-being.
This phenomenon can be observed among different patient populations.
In recent years, researchers have begun to describe people addicted to tanning, at least according to criteria set out by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for substance-related disorders.19) One research team calls the addiction “UV light substance-related disorder.”20) A 2010 study suggests individuals who have used indoor tanning facilities may meet criteria for addiction, and may also be more prone to anxiety symptoms and substance use.21) Among 229 study participants (students at a northeastern U.S. college) who had used indoor tanning facilities, the average number of visits during a given year was 23. A total of 90 (39.3 percent) met criteria for tanning addiction on one measure and 70 (30.6 percent) met criteria on the other measure. Students who did meet these criteria were more likely to report symptoms of anxiety and use of alcohol, marijuana and other substances than those who did not meet these criteria.
If associations between affective factors and indoor tanning behavior are replicated, results suggest that treating an underlying mood disorder may be a necessary step in reducing skin cancer risk among those who frequently tan indoors. Researchers have hypothesized that those who tan regularly year round may require more intensive intervention efforts, such as motivational interviewing, relative to those who tan periodically in response to mood changes or special events.
Catherine E. Mosher, Ph.D. and Sharon Danoff-Burg, Ph.D.22)
Whether it is an addiction or dependency, the Marshall Pathogenesis states that people who experience symptom relief following light exposure are being immunosuppressed.
Conversely, when a patient's 1,25-D is reduced, activity of the innate immune system increases as do symptoms of disease. This can be seen in people said to suffer from seasonal affective disorder (SAD), a mood disorder in which people who have normal mental health throughout most of the year experience depressive symptoms in the winter.
Patients experiences
My mood improved seriously when I started wearing NoIRsSpecial sunglasses worn by Marshall Protocol patients to block light., the most powerful antidepressivum I ever used. Did not start the benicar yet. The antidepressive effect of avoiding bright light is an impressive proof for 1,25D being involved in depression.
Nightshade, MarshallProtocol.com
The “sparkle” is back. Now I don't feel depressed at all like I have in years past. No more SAD.
DThomas, MarshallProtocl.com
When I started Benicar [which lowers 1,25-D], my mood went way up as stress and anxiety went down. Felt like my brain had a big pressure load removed with the Benicar, and I mellowed right out. I have seen a number of people say that their moods improved tremendously when they started the Benicar.
Penny, MarshallProtocol.com
Read more
- "Why Am I Sick?" (Nudist Forum) - a number of devoted nudists complain about their symptoms of inflammatory disease
- Too Much Sunshine Spurs Suicides in Arctic, Study Says – review of a 2009 BMC Psychiatry article,23) which showed that suicide was much more common among Greenland residents in the summer than the winter months
- Children born and living without sunlight – In 2012, it was learned that 27 children had been living underground as members of a Muslim sect. Many had lived there for their entire lives and had never seen daylight. The conditions of these children was pronounced as “satisfactory” by pediatricians
[PMID: 19655431] [DOI: 10.1016/s1470-2045(09)70213-x]
[PMID: 17688099] [DOI: 10.2466/pr0.100.3.810-814]
[PMID: 11805594] [DOI: 10.1097/00001648-200201000-00017]
[PMID: 9718233] [DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1998.tb10048.x]
[PMID: 12103450] [DOI: 10.1016/s0165-0327(00)00373-6]
[PMID: 8352350] [DOI: 10.1176/ajp.150.9.1380]
[PMID: 2960714] [DOI: 10.1016/0165-0327(87)90040-1]
[PMID: 9241572] [DOI: 10.1016/s0165-0327(97)00035-9]
[PMID: 15575348] [DOI: 10.1007/s10654-004-4695-8]
[PMID: 2326139] [DOI: 10.2466/pms.1990.70.1.57]
[PMID: 16504069] [PMCID: 1397811] [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-6-40]
[PMID: 16234425] [PMCID: 1732944] [DOI: 10.1136/jech.2004.030981]
[PMID: 10030056] [DOI: 10.1590/s0034-89101998000500002]
[PMID: 9061800] [DOI: 10.1016/s0165-1781(96)02974-5]
[PMID: 20415738] [DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0781.2010.00492.x]
[PMID: 21323660] [PMCID: 3074219] [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04315.x]
[PMID: 21375518] [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.10161.x]
[PMID: 21243005] [DOI: 10.1038/icb.2010.170]
[PMID: 19152511] [DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0781.2009.00392.x]
[PMID: 17257709] [DOI: 10.1016/j.jaad.2006.08.064]
[PMID: 20404230] [PMCID: 3756887] [DOI: 10.1001/archdermatol.2009.385]
[PMID: 11735320] [DOI: 10.1054/mehy.2001.1423]